3,4-Dihydropyran

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3,4-Dihydro-2H-pyran | |
| Other names
2,3-Dihydro-4H-pyran, DHP
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.465 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2376 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H8O | |
| Molar mass | 84.118 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.922 g/mL |
| Melting point | −70 °C (−94 °F; 203 K) |
| Boiling point | 86 °C (187 °F; 359 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H225, H315, H317, H319 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P272, P280, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338, P321, P332+P313, P333+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
3,4-Dihydropyran (DHP) is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C5H8O. The six-membered C5O ring has the unsaturation adjacent to oxygen. The isomeric 3,6-dihydropyran has a methylene separating the double bond and oxygen. DHP is used for protecting group for alcohols. It is a colorless liquid.[1]
Preparation
[edit]Dihydropyran is prepared by the dehydration of tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol over alumina at 300–400 °C.[2] THFA is itself prepared from tetrahydro-2-furoic acid.
Reactions
[edit]In organic synthesis, the 2-tetrahydropyranyl (THP) group is used as a protecting group for alcohols.[3][4] Reaction of the alcohol with DHP forms a THP ether, protecting the alcohol from a variety of reactions. The alcohol can later be restored by acidic hydrolysis, concomitant with formation of 5-hydroxypentanal.[5]
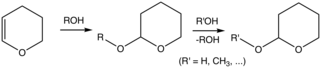
Protection of an alcohol as THP ether followed by its deprotection. Both steps require acid catalysts.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Paul Ch. Kierkus (2001). "3,4-Dihydro-2H-pyran". EEROS. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rd230. ISBN 0471936235.
- ^ R. L. Sawyer and D. W. Andrus (1955). "2,3-Dihydropyran". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 3, p. 276.
- ^ R. A. Earl L. B. Townsend (1990). "Methyl 4-Hydroxy-2-butynoate". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 7, p. 334.
- ^ Arthur F. Kluge (1990). "Diethyl [(2-Tetrahydropyranyloxy)methyl]phosphonate". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 7, p. 160.
- ^ Wuts, Peter G. M.; Greene, Theodora W. (2006). "Protection for the Hydroxyl Group, Including 1,2- and 1,3-Diols". Greene's Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis (4th ed.). pp. 16–366. doi:10.1002/9780470053485.ch2. ISBN 9780470053485.


